Stock Splits and Reverse Splits: What You Need to Know
Stock splits and reverse splits are popular ways companies manage their stock. These two impact stock prices and holdings making them a big deal to any investor. In this article, we’ll break down stock splits and reverse stock splits. Staying with it till the end will equip you with the knowledge to navigate these corporate actions confidently.
What Are Stock Splits?
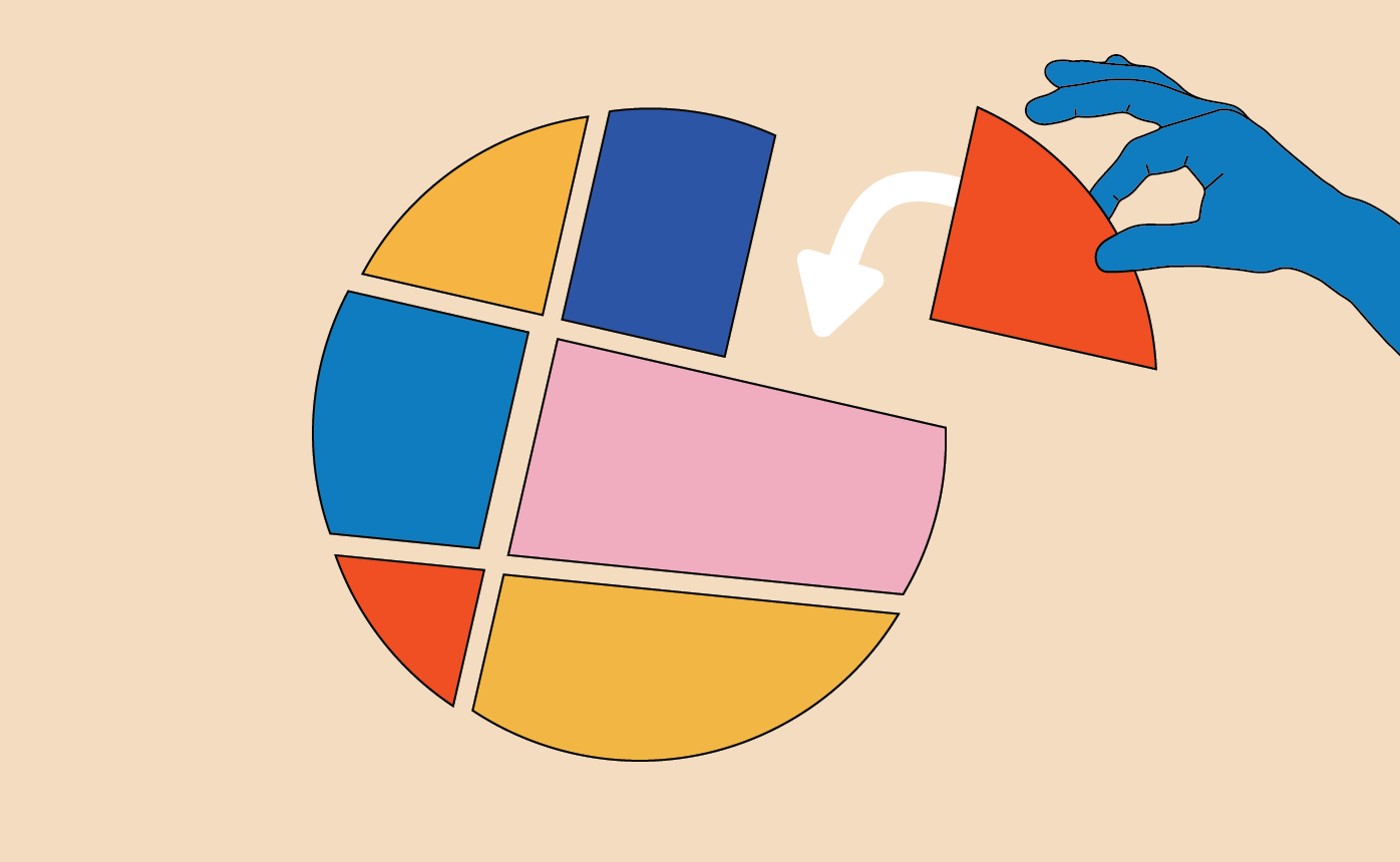
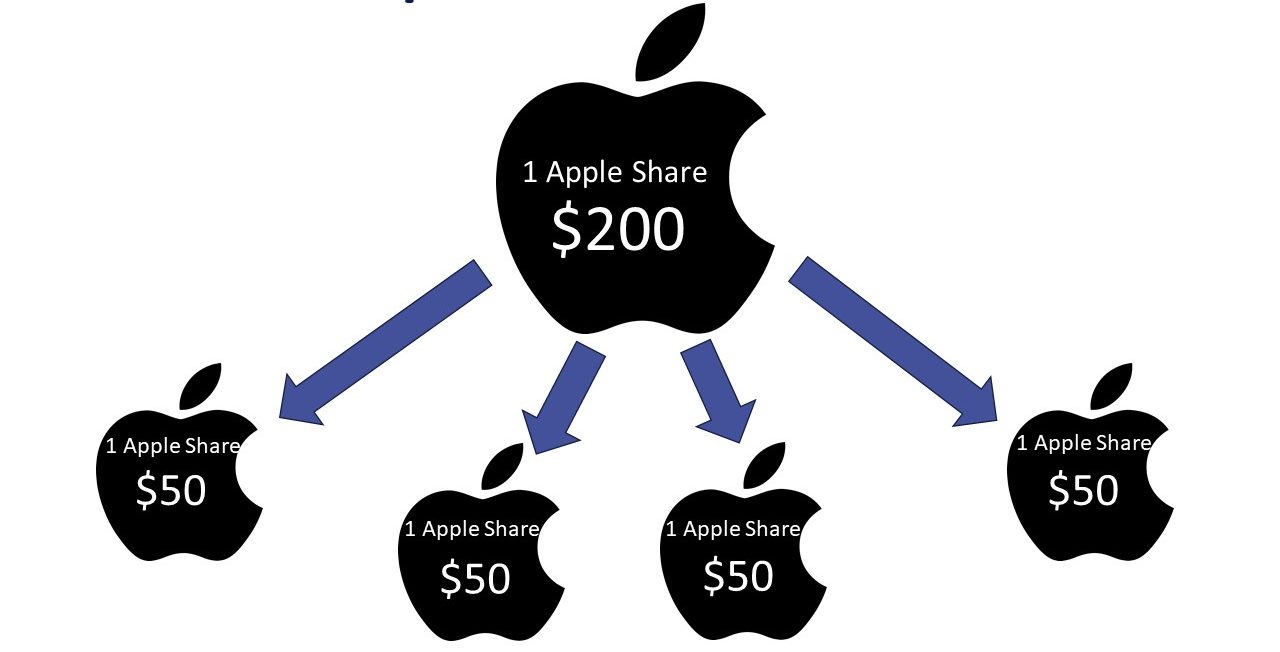
A stock split is when a company increases its outstanding shares while lowering the price of each. For example, in a 2-for-1 stock split, you’d get two shares for every share you owned before, and the price would fall by half.
Types of Stock Splits
Stock splits typically follow a ratio, like 2-for-1, 3-for-1, or even higher ones. The most common is the 2-for-1 split. But some companies opt for more aggressive splits, like 3-for-1 or even 4-for-1, to increase the accessibility of their shares.
How Stock Splits Work
Stock splitting is a straightforward process. First, the company announces its intention to do so. Then, it sets a date to determine eligibility. After the split, shareholders receive their additional shares, and the price adjusts proportionately.
For context, let’s say Company X announces a 3-for-1 stock split when its stock is trading at $90 per share. After the split, each shareholder will receive two additional shares for each owner. If you owned 100 shares before, you’ll now have 300.
However, the share price will fall to $30 (1/3 of the pre-split price). The company’s market capitalization remains the same, but the number of outstanding shares has tripled.
Why Do Companies Split Their Stocks?
Companies split their stocks for a few key reasons:Making shares more affordable:
- High share prices can put off some investors, so a split makes them cheaper, potentially attracting more buyers.
- Increased liquidity: More shares in the market can increase trading and the company’s liquidity.
- Positive signal: Splits often indicate that the company is doing well and is confident about its future.
Impact on Shareholders
As we’ve seen, stock splitting changes a company’s total number of shares and their prices. That said, the overall value of your investment stays the same. If you owned 10 shares worth $100 each before a 2-for-1 split, you’d own 20 shares worth $50 afterward – the total value remains $1000.
Psychological Effects and Investor Perception
Stock splits can have a psychological impact on market sentiment and behavior. When investors perceive share price lowly, they may view the stock as more affordable and attractive. That can lead to increased demand and trading volume.
However, it’s important to remember that stock splits don’t necessarily indicate a company’s future performance. That’s despite some investors seeing them as a positive signal by the market. Still, a company’s fundamentals and growth prospects should be the primary drivers of investment decisions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Splits
Companies and investors can gain a lot from stock splits. The former can:
- Increase their liquidity
- Broaden the investor base
- Potentially boost trading volume.
And for investors, they:
- Make shares more accessible potentially increasing their demand,
- Lead to a share price appreciation.
On the other hand, stock splits also have some drawbacks:
- Companies can find them costly to execute.
- there’s no guarantee that they’ll have the desired effect on trading volume or share price appreciation.
- Some investors may take stock splits to signal that a company’s growth potential has peaked. This could negatively impact investor sentiment.
What Are Reverse Stock Splits?
A reverse stock split is the opposite of a traditional split. Here the company reduces the number of shares out there and increases the share price proportionally. In a 1-for-10 reverse split for instance, your 10 shares become 1 share, but the price would jump ten times.
Companies with low share prices often use them to avoid delisting from stock exchanges with minimum share price requirements. By reducing the number of outstanding shares, their share price rises, meeting the exchange’s listing requirements.
How do Reverse Splits Work?
The process is similar to a regular stock split, but in reverse. It starts with the company announcing its intention to conduct the split. It then sets a date and then consolidates the shares accordingly.
For example, Company Y may announce a 1-for-5 reverse split when its stock is trading at $1 per share. After the process, shareholders will receive one new share for every five they previously owned.
So,if you owned 1,000 shares before, you’ll now have 200. But the share price will rise to $5 per share (5 times the pre-split price).
Reasons for Reverse Splits
Several reasons could compel a company to reverse split its shares. The most prominent ones are:
- Low share price: Institutional investors sometimes consider share prices under $5 unattractive. Thus, a reverse split bumps the price, restoring their confidence.
- Avoiding delisting: Stock exchanges can delist companies with very low share prices. Nasdaq for instance may delist stocks that have persistently traded under a dollar relegating them to penny stocks. Reverse splits can help such companies meet the exchange’s price requirements.
Impact of Reverse Stock Splits
Like stock splits, reverse splits don’t change your investment’s overall value. However, they often carry a negative stigma, since struggling companies may use them to bump their share prices. This negative perception can lead to declining trade volumes and liquidity, exacerbating the company’s challenges.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reverse Stock Splits
For companies performing them, reverse stock splits can be a boon:
- Importantly, they enable them to follow exchange listing requirements.
- Moreover, they increase the possibilities of attracting institutional investors who see value in the enhanced stock prices.
Conversely, they may paint a picture of a fallen stock which is off putting to some investors.
- This negative perception could reduce their trading volumes and liquidity.
- Finally, the bumped up stock prices may be expensive for investors.
Key Considerations for Investors
As an investor, it’s crucial to understand the reasons behind a company’s decision to split or reverse split its stock. These actions, as we’ve seen earlier, can have significant implications for your investment strategy and portfolio management.
So, when evaluating them, consider the company’s overall financial health, growth prospects, and competitive position. A stock split shouldn’t be the sole reason for investing in a company, as it doesn’t necessarily indicate future performance.
Similarly, you shouldn’t automatically take a reverse stock split as a negative signal. Instead, analyze the company’s underlying fundamentals and reasons behind the decision before making investment decisions.
Using Stock Splits and Reverse Splits in Investments
As a beginner investor, it’s essential to have a well-defined strategy when navigating both splits. Here are some tips to help you along:
- Stay abreast of any upcoming stock or reverse splits. This will help you prepare and adjust your investment strategy accordingly.
- Understand the rationale: Try to understand the company’s motivations behind the decision. Is it a positive move looking to increase liquidity or attract new investors? Or is it a potential red flag indicating financial distress?
- Evaluate the fundamentals: Research on the company’s financial health, growth prospects, and competitive landscape to make an informed choice.
- Consider your investment goals: If a split or reverse split doesn’t align with your objectives, it may be wise to reevaluate your position in the stock.
- Consult a financial advisor: Unsure how to proceed? Seek guidance from a qualified financial advisor who can provide personalized advice.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
To better illustrate the concepts of stock splits and reverse splits, let’s explore some real-world examples and case studies:
1. Apple Inc. (AAPL): In 2020, the tech giant announced a 4-for-1 stock split, increasing its outstanding shares from around 4.5 to 18 billion. Investors saw this move as a positive signal by the market, reflecting Apple’s confidence in its growth prospects.
2. Citigroup Inc. (C): In 2011, Citigroup announced a 1-for-10 reverse stock split to boost its share price and avoid delisting from the NYSE. The move sought to restore waning investor confidence in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis.
3. Groupon Inc. (GRPN): In 2016, Groupon underwent a 1-for-20 reverse stock split to follow NASDAQ’s minimum share price requirement of $1 per share. This move helped it maintain its listing status. Unfortunately, some interpreted it as highlighting Groupon’s struggles to maintain profitability and growth.
Conclusion
Stock and reverse splits are tools companies use to restructure their shares. While they can cause short-term excitement and changes in share price, it’s essential to remember that they don’t fundamentally alter a company’s value. As an investor, always prioritize the big picture: a company’s financial health, long-term prospects, and competitive position.
FAQs
How do you understand a reverse split?
In a reverse split, a company consolidates smaller-priced shares into fewer, bigger-priced ones.
Is it advisable to buy before or after a reverse stock split?
Neither is inherently better. Instead, focus on whether the company is a good investment.
Why do investors dislike reverse splits?
Companies in distress often use reverse splits hence the negative association.
Should I sell my stock after a reverse split?
Don’t sell just because of a reverse split. Analyze the company’s overall health and whether it fits your investment strategy

Updated Apr 14, 2024
Contents

Sign up for our newsletter
Join our exclusive community of over one million investment enthusiasts and receive our free newsletter filled with analysis, news, and updates every weekday.












 All stocks
All stocks
 All Stocks
All Stocks
 52-Week High
52-Week High
 52-Week Low
52-Week Low
 AI Companies
AI Companies
 Big Tech
Big Tech
 Death Cross Stocks
Death Cross Stocks
 Golden Cross Stocks
Golden Cross Stocks
 High Beta
High Beta
 High Dividend
High Dividend
 High Volume
High Volume
 Highest Cash
Highest Cash
 Highest EBITDA
Highest EBITDA
 Highest NET Income
Highest NET Income
 Highest Revenue
Highest Revenue
 Largest Employers
Largest Employers
 Most Expensive
Most Expensive
 Most Volatile
Most Volatile
 Tech Companies 2024
Tech Companies 2024
 Triangle Patterns Stocks
Triangle Patterns Stocks
 All ETFs
All ETFs
 All ETFs
All ETFs
 Energy Sector ETFs
Energy Sector ETFs
 Major World ETFs
Major World ETFs
 Top US ETFs
Top US ETFs
 All Tools
All Tools
 Alerts
Alerts
 Technical Signals
Technical Signals
 Score
Score
 Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio
 Candle and Chart Patterns
Candle and Chart Patterns